IPS stem cell
I. 소개
A. iPS 세포의 정의
iPS 세포는 신체의 모든 세포 유형으로 분화할 수 있는 능력을 가진 줄기 세포 유형입니다. 2006년 선구적인 연구로 2012년 노벨 생리의학상을 수상한 야마나카 신야(Shinya Yamanaka)가 처음 발견했습니다.
B. 의학 연구에서 iPS 세포의 중요성
iPS 세포는 과학자들이 인간 피험자나 동물 모델 없이도 접시에서 질병을 연구하고 치료법을 개발할 수 있게 해주기 때문에 의학 연구에 엄청난 잠재력을 가지고 있습니다. 또한 손상된 조직을 복구하는 데 필요한 모든 세포 유형으로 분화하도록 유도할 수 있으므로 재생 의학에 사용될 가능성이 있습니다.
C. Google에서 iPS 세포가 많이 노출되는 이유에 대한 설명
iPS 세포는 발견 이후 이 분야에 집중된 엄청난 양의 연구와 언론의 관심으로 인해 Google에 많이 노출되어 있습니다. iPS 세포의 잠재적 응용 분야는 광범위하고 대중의 상상력을 사로잡아 미디어와 인터넷에서 인기 있는 토론 주제가 되었습니다.
II. iPS 세포란 무엇입니까?
A. iPS 세포의 기원
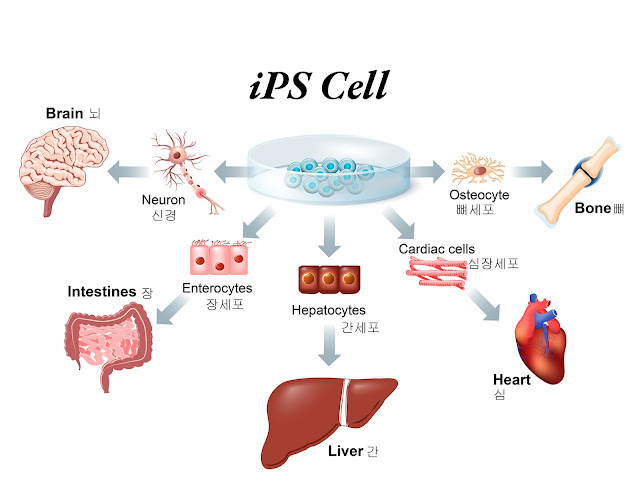
iPS 세포는 특정 유전자 집합을 도입하여 배아와 유사한 상태로 재프로그래밍된 피부 또는 혈액 세포와 같은 성인 세포에서 생성됩니다. 생성된 세포는 배아 줄기 세포처럼 체내의 모든 세포 유형으로 분화할 수 있는 다능성 세포입니다.
B. iPS 세포의 특성
iPS 세포는 의학 연구에 특히 유용한 몇 가지 주요 특성을 가지고 있습니다. 그들은 불멸하며 실험실에서 무한정 성장할 수 있음을 의미하며 유전적으로 환자와 동일하므로 맞춤형 의료에 유용합니다.
다. 배아줄기세포와의 비교
iPS 세포는 다능성 및 신체의 모든 세포 유형으로 분화할 수 있는 능력을 포함하여 여러 면에서 배아 줄기 세포와 유사합니다. 그러나 배아에서 얻은 배아 줄기 세포와 달리 iPS 세포는 성체 세포에서 생성할 수 있어 배아 줄기 세포 연구와 관련된 윤리적, 정치적 논쟁을 피할 수 있습니다.
III. iPS 세포 생성 방법
A. 프로세스 개요
iPS 세포를 생성하는 과정에는 바이러스 벡터 또는 기타 방법을 사용하여 특정 유전자 세트를 성체 세포에 도입하는 것이 포함됩니다. 그런 다음 세포는 실험실에서 성장하고 특정 마커의 발현과 같은 만능성 징후에 대해 모니터링됩니다.
B. 다른 방법의 장단점
iPS 세포를 생성하는 다양한 방법에는 프로세스의 효율성, 세포의 안전성 및 오염 가능성을 포함하여 서로 다른 장점과 단점이 있습니다. iPS 세포 기술의 최근 발전으로 비바이러스 벡터 및 소분자의 사용을 포함하여 더 안전하고 효율적인 방법이 개발되었습니다.
C. iPS 세포 기술의 최근 발전
최근 몇 년 동안 iPS 세포를 생성하는 보다 효율적이고 안전한 방법의 개발, 더 넓은 범위의 세포 유형에서 iPS 세포를 생성하는 능력, 특정 유전자 변형. 이러한 진보는 의학 연구 및 재생 의학에서 iPS 세포의 잠재적인 응용 분야를 크게 확장했습니다.
IV. iPS 세포의 응용
A. 질병 모델링 및 약물 발견 가능성
iPS 세포는 우리가 질병을 연구하고 치료하는 방식을 혁신할 수 있는 잠재력을 가지고 있습니다. 이를 통해 과학자들은 실험실에서 질병을 모방하는 세포를 생성할 수 있으며, 이를 통해 질병의 기본 메커니즘을 연구하고 새로운 치료법을 개발할 수 있습니다. iPS 세포는 이미 암, 심혈관 질환 및 신경 장애를 포함한 광범위한 질병을 모델링하는 데 사용되었습니다.
B. 재생 의학의 가능성
iPS 세포는 손상된 조직을 복구하는 데 필요한 모든 세포 유형으로 분화되도록 유도할 수 있기 때문에 재생 의학에 엄청난 잠재력을 가지고 있습니다. 이것은 심장 질환, 파킨슨 병 및 척수 손상을 포함한 광범위한 상태를 치료하는 데 사용될 가능성이 있습니다.
C. 맞춤형 의학의 가능성
iPS 세포는 환자 자신의 세포에서 생성될 수 있으므로 개인 맞춤형 의료를 위한 이상적인 도구입니다. 이를 통해 각 환자의 특정 유전적 배경에 맞는 치료법을 개발할 수 있어 성공 가능성을 높이고 부작용 위험을 최소화할 수 있습니다.
V. 안전 문제 및 제한 사항
A. 안전 문제
잠재력에도 불구하고 iPS 세포에 안전 문제가 없는 것은 아닙니다. 세포를 재프로그래밍하는 데 사용되는 유전자가 적절하게 조절되지 않으면 세포가 암이 될 위험이 있습니다. 재생 의학에 사용되는 경우 환자의 면역 체계에 의해 세포가 거부될 위험도 있습니다.
나. 제한사항
iPS 세포의 사용에는 리프로그래밍 프로세스의 효율성과 세포를 치료용으로 적합하게 만들기 위한 추가적인 유전적 변형의 필요성을 포함하여 몇 가지 기술적 한계가 있습니다. 또한 iPS 세포에 대해 아직 알려지지 않은 부분이 많으며 잠재력과 한계를 완전히 이해하기 위해서는 추가 연구가 필요합니다.
VI. 결론
iPS 세포는 의학 연구 및 재생 의학을 위한 강력한 도구이며 우리가 질병을 연구하고 치료하는 방식을 혁신할 수 있는 엄청난 잠재력을 가지고 있습니다. 그러나 여전히 해결해야 할 미지수와 안전 문제가 많기 때문에 신중하게 진행하는 것이 중요합니다. 이러한 문제에도 불구하고 iPS 세포는 광범위한 질병에 대한 보다 효과적이고 개인화된 치료법을 찾는 데 있어 중요한 단계입니다.
I. Introduction
A. Definition of iPS Cells
iPS cells are a type of stem cell that have the ability to differentiate into any cell type in the body. They were first discovered in 2006 by Shinya Yamanaka, who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2012 for his pioneering work.
B. Importance of iPS Cells in Medical Research
iPS cells have enormous potential for medical research, as they allow scientists to study diseases and develop treatments in a dish, without the need for human subjects or animal models. They also have the potential to be used for regenerative medicine, as they can be induced to differentiate into any cell type needed to repair damaged tissues.
C. Explanation of Why iPS Cells are Highly Exposed in Google
iPS cells are highly exposed in Google because of the vast amount of research and media attention that has been devoted to this field since its discovery. The potential applications of iPS cells are far-reaching and have captured the public imagination, making them a popular topic of discussion in the media and on the internet.
II. What are iPS Cells?
A. Origin of iPS Cells
iPS cells are generated from adult cells, such as skin or blood cells, that are reprogrammed to an embryonic-like state by introducing a set of specific genes. The resulting cells are pluripotent, meaning that they can differentiate into any cell type in the body, just like embryonic stem cells.
B. Characteristics of iPS Cells
iPS cells have several key characteristics that make them particularly useful for medical research. They are immortal, meaning that they can be grown in the laboratory indefinitely, and they are genetically identical to the patient from whom they were derived, making them useful for personalized medicine.
C. Comparison with Embryonic Stem Cells
iPS cells are similar to embryonic stem cells in many ways, including their pluripotency and ability to differentiate into any cell type in the body. However, unlike embryonic stem cells, which are obtained from embryos, iPS cells can be generated from adult cells, avoiding the ethical and political controversy associated with embryonic stem cell research.
III. Methods for Generating iPS Cells
A. Overview of the Process
The process of generating iPS cells involves introducing a set of specific genes into adult cells using viral vectors or other methods. The cells are then grown in the laboratory and monitored for signs of pluripotency, such as the expression of certain markers.
B. Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Methods
Different methods for generating iPS cells have different advantages and disadvantages, including the efficiency of the process, the safety of the cells, and the potential for contamination. Recent advances in iPS cell technology have led to the development of safer and more efficient methods, including the use of non-viral vectors and small molecules.
C. Recent Advances in iPS Cell Technology
In recent years, there have been many advances in iPS cell technology, including the development of more efficient and safe methods for generating iPS cells, the ability to generate iPS cells from a wider range of cell types, and the ability to generate iPS cells with specific genetic modifications. These advances have greatly expanded the potential applications of iPS cells in medical research and regenerative medicine.
IV. Applications of iPS Cells
A. Potential for Disease Modeling and Drug Discovery
iPS cells have the potential to revolutionize the way we study and treat diseases. They allow scientists to generate cells that mimic the disease in the laboratory, which can then be used to study the underlying mechanisms of the disease and develop new treatments. iPS cells have already been used to model a wide range of diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders.
B. Potential for Regenerative Medicine
iPS cells have enormous potential for regenerative medicine, as they can be induced to differentiate into any cell type needed to repair damaged tissues. This has the potential to be used to treat a wide range of conditions, including heart disease, Parkinson's disease, and spinal cord injury.
C. Potential for Personalized Medicine
iPS cells can be generated from a patient's own cells, making them an ideal tool for personalized medicine. This allows for the development of treatments that are tailored to the specific genetic background of each patient, increasing the chances of success and minimizing the risk of adverse side effects.
V. Safety Concerns and Limitations
A. Safety Concerns
Despite their potential, iPS cells are not without their safety concerns. There is a risk of the cells becoming cancerous if the genes used to reprogram them are not properly regulated. There is also a risk of the cells being rejected by the patient's immune system if they are used for regenerative medicine.
B. Limitations
There are also several technical limitations to the use of iPS cells, including the efficiency of the reprogramming process and the need for additional genetic modifications to make the cells suitable for therapeutic use. In addition, there is still much that is unknown about iPS cells, and further research is needed to fully understand their potential and limitations.
VI. Conclusion
iPS cells are a powerful tool for medical research and regenerative medicine, and they have enormous potential to revolutionize the way we study and treat disease. However, it is important to proceed with caution, as there are still many unknowns and safety concerns to be addressed. Despite these challenges, iPS cells represent a major step forward in the quest for more effective and personalized treatments for a wide range of diseases.

댓글
댓글 쓰기